SMILE – Towards Smarter Network Edges for Next Generation Networks
Overview
As the number of smart devices and their applications continue to growth, transmission of mobile traffic data over wireless links (i.e., Wi-Fi and cellular links) is exploding. A recent Cisco report predicts that by 2019, enough mobile devices will exist to create more than 24 exabytes (24,000,000 terabytes) of traffic per month. Among the different wireless interfaces of smart devices, Wi-Fi interface will be the prominent network interface to connect smart devices and their users to the Internet. For example, a recent study found that Wi-Fi networks are expected to carry almost 60% of smartphone and tablet data traffic by 2019. Moreover, the large amount of data generated by end devices has triggered service migration from the cloud to the edge of the network. The objective of this new edge computing trend is to enhance the user’s quality of experience. To cope with the explosion of mobile devices coupled with a growing proliferation of cloud or edge-based applications, best-effort Quality Of Service (QoS) is no longer a satisfactory solution and a new breed of intelligent networks is required. More specifically, it is now necessary to have greater visibility and control over the traffic generated from the client devices in order to deliver optimal performance and a high Quality of Experience (QoE) to a variety of users and applications.
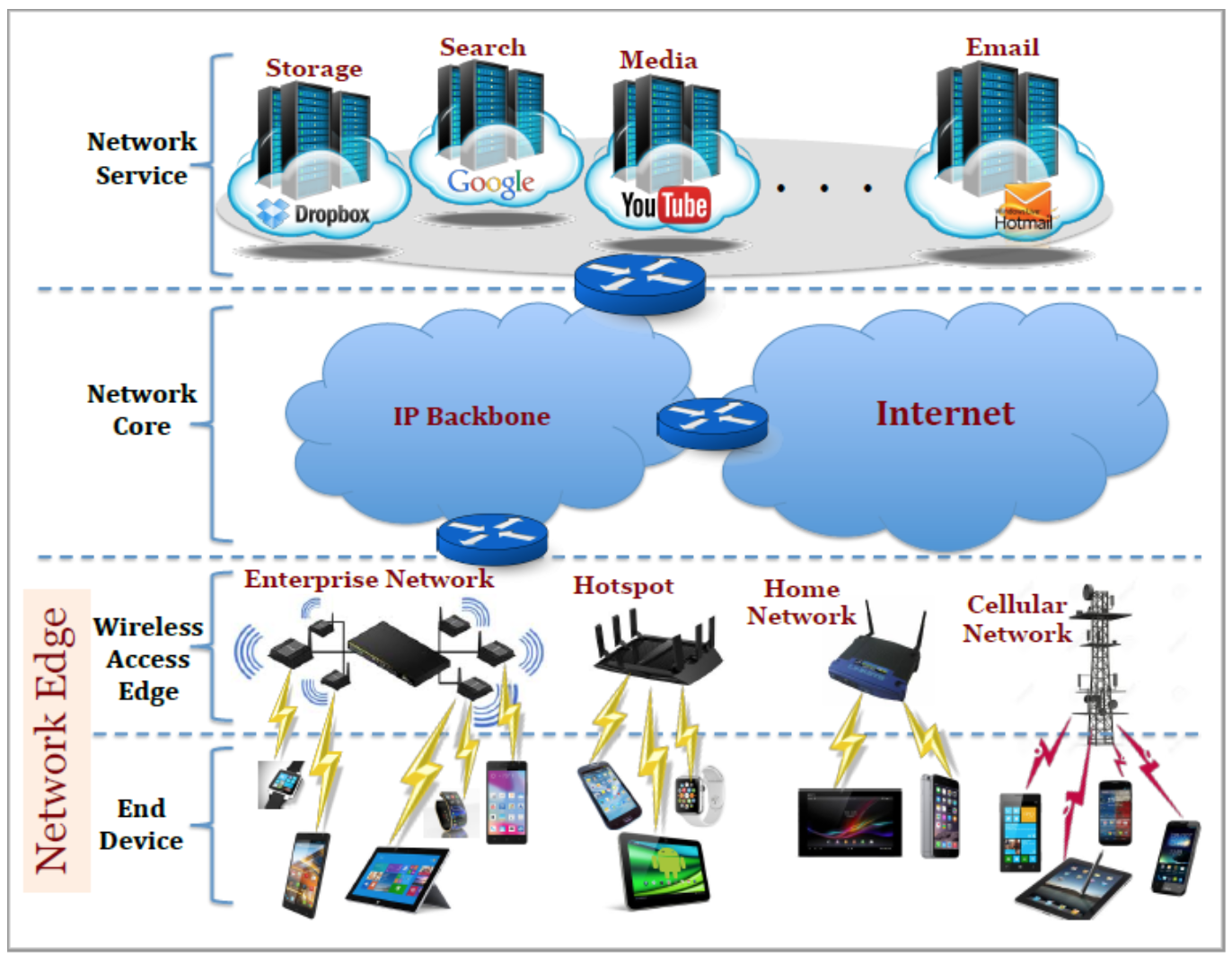
Recently, networks community embraced the Software Defined Network (SDN) approach for designing and managing wired networks in order to respond rapidly and deliver performance guarantees to end users by dynamically orchestrating services and policies on network routers and switches. We argue that both network wireless-edges and end-devices, which construct Network Edge as shown in Figure 1, need to become more intelligent with respect to networking in order to facilitate a quality user experience. More specifically, we believe that an SDN-like paradigm needs to be pushed to wireless-edges and mobile clients to provide optimal network performance between the cloud and wirelessly connected clients. In addition, cloud services need to be partially pushed to the wireless-edges to be closer to the user to support scalability and fast adaptation to various user requirements. In this project, we aim to design, develop and evaluate SMILE - SMart and Intelligent wireLess Edge framework that supports SDN-like paradigm on user's smart devices and network wireless-edges. SMILE enables network wireless-edges to become more active and to host several services (including partial cloud services) to enhance users quality of experience.
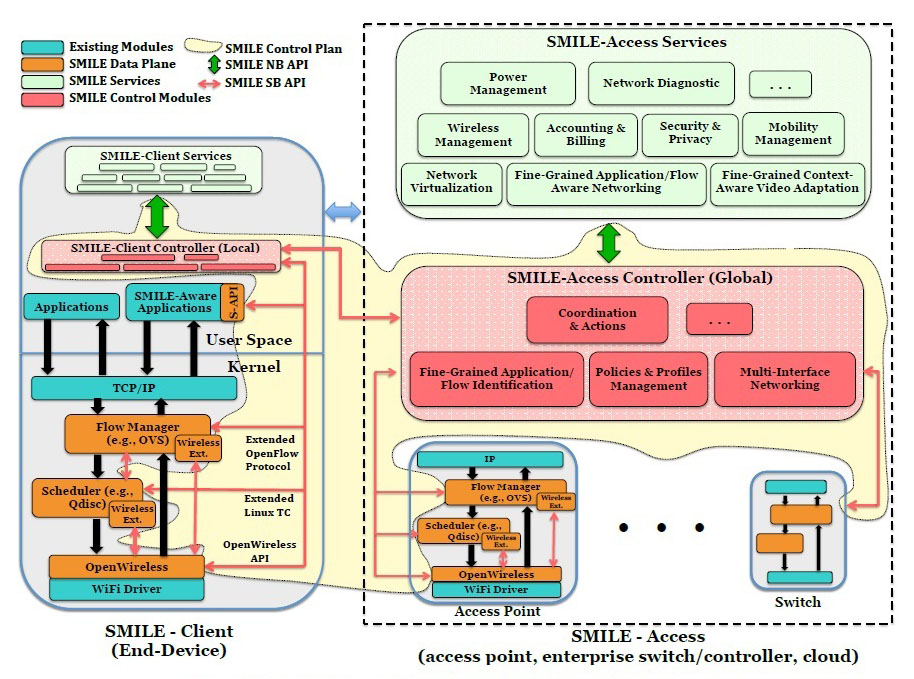
Figure 2 shows the proposed SMILE framework that mainly consists of SMILE-Client that runs on end-devices and SMILE-Access that runs on access devices at the network edge. SMILE modules are divided into two main components: SMILE data plane and SMILE control plane. SMILE data plane consists of forwarding network components on wireless access points, client devices, and enterprise switches/routers. On the other hand, SMILE control plane consists of Northbound-API (NB API), Southbound-API (SB API), local controllers (SMILE Client Controllers) running on end-devices, and the global controller (SMILE Access Controller) that could run on access points in case of Wi-Fi home networks, on switches/controllers in case of Wi-Fi enterprise networks, or in cloud in case of Wi-Fi hotspots or cellular networks. SMILE control plane is a logically centralized entity in charge of managing and controlling/programming SMILE data plane through Southbound API while providing abstract network views through Northbound API to network applications and services. SMILE supports wireless networks to be open, flexible, and programmable to cope with complexity, dynamic nature, and uncertainty associated with wireless networks. Moreover, SMILE framework allows the wireless network to be managed in harmony with their wired counterparts.
Funding
- NSF CNS 1764185: "NeTS: Small: SMILE -- Towards Smarter Network Edges for Next Generation Networks”
Documentation
- FlexStream: Towards Flexible Adaptive Video Streaming on End Devices using Extreme SDN" at ACM MM conference, November 2018. (FlexStream Slides)
- FlexStream: Towards Flexible Adaptive Video Streaming on End Devices using Extreme SDN" at ACM MM conference, November 2018. (FlexStream Poster)
- Towards Smarter and Flexible Network Edges using Extreme SDN" at KAIST University, Korea, November 2018. (KAIST Slides)
- PrivacyGuard: Extreme SDN Framework for IoT and Mobile Applications Flexible Privacy at the Edge" at IEEE PerCom Conference, March 2019. (PrivacyGuard Slides)
Publications
- Santosh Nukavarapu and Tamer Nadeem, “Securing Edge-based IoT Networks with Semi-Supervised GANs”, The 5th IEEE International Workshop on Smart & Green Edge Computing and Networking (SmartEdge) in conjunction with the 2021 IEEE Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), Kassel, Germany, March 2021. (Accepted)
- Hannaneh Pasandi, Tamer Nadeem. "Towards a Learning-Based Framework for Self-Driving Design of Networking Protocols", IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 34829-34844, February 2021.
- Hannaneh B. Pasandi and Tamer Nadeem, "CONVINCE: Collaborative Cross-Camera Video Analytics at the Edge," 2020 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Austin, TX, USA, 2020.
- Hannaneh Pasandi, Tamer Nadeem. "Mac protocol design optimization using deep learning", The 2nd IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC 2020), Fukuoka, Japan, February 19-21, 2020.
- Ahmed Nasr, Tamer Nadeem. "A Novel Technique for Gait Analysis using Two Waist Mounted Gyroscopes". The 38th IEEE Global Communications Conference (Globecom), Waikoloa, HI, USA, December 9-13, 2019.
- Mostafa Uddin, Tamer Nadeem, Santosh Nukavarapu, "Extreme SDN Framework for IoT and Mobile Applications Flexible Privacy at the Edge", The 17th IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom’19), Kyoto, Japan, March 11 - 15, 2019.
- Ibrahim Ben Mustafa, Tamer Nadeem, and Emir Halepovic. "FlexStream: Towards Flexible Adaptive Video Streaming on End Devices using Extreme SDN". In 2018 ACM Multimedia Conference (MM ’18), October 22–26, 2018, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- Ibrahim Ben Mustafa, Tamer Nadeem. "Programmable and Flexible Adaptive Video Streaming using Extreme SDN", ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications. (Under journal preparation/submission)
- Tamer Nadeem, Mostafa Uddin, Santosh Nukavarapu. "PrivacyGuard: Towards Flexible Edge Privacy Framework for IoT and Mobile Applications using Extreme SDN", IEEE Access. (Under journal preparation/submission)
- Nukavarapu, Santosh and Nadeem, Tamer. "iKnight - Guarding IoT infrastructure using Generative Adversarial Networks". (Under journal preparation/submission)
Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.